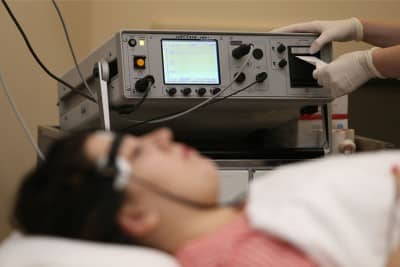
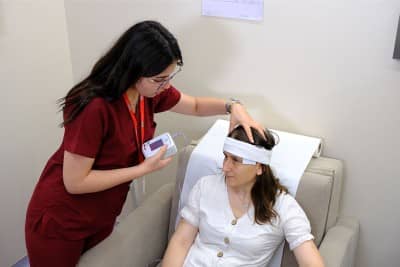
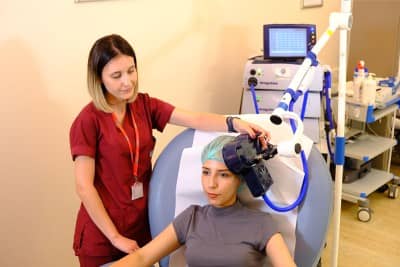
Psychiatry is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mental, emotional and behavioral disorders. Psychiatrists are doctors who have medical training and specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. This specialty evaluates and treats patients' mental health conditions using a comprehensive approach that combines biological, psychological and social factors. Psychiatrists provide individualized treatment, including medication, psychotherapy and neuromodulation therapies. The treatment plan is customized according to the patient's individual needs and current condition.
What is Psychiatry?
Psychiatry is a branch of science that deals with diseases of the brain and mental disorders. This field aims to diagnose and treat what are colloquially referred to as mental disorders or mental illnesses, which are characterized by differences in thoughts, actions and feelings. Psychiatry is concerned with the correct diagnosis of these disorders and the application of appropriate treatment methods.
Specialized psychiatrists working in clinics often work in collaboration with psychologists to make the treatment process more effective. These clinics use various assessment methods such as counseling services for children and families, adolescent counseling, personalized tests, intelligence and development tests for children (MMPI, TAT, WISC-R, AGTE). In addition, therapy methods such as play therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy and EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) are also used. These various tests and therapies are tailored to the individual needs of patients and are used to provide them with the most appropriate support.
What are Psychiatric Diseases?
The field of psychiatry, which can be briefly defined as mental health and diseases, is examined in 2 categories: child and adolescent psychiatry and adult psychiatry. Adult psychiatry aims to diagnose and treat mental disorders in individuals aged 18 and over. Child and adolescent psychiatry is the field of psychiatry that aims to diagnose and treat mental disorders in children and adolescents under the age of 18. We can list these psychiatric diseases as follows;
- Addiction
- Depression
- Psychotic disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Bipolar mood disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Post-traumatic stress disorders
- Anxiety disorder
- Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Paranoia
- Geriatric disorder (diseases of old age)
- Sleep problems
Child and adolescent psychiatric disorders
- Down syndrome
- Peer bullying
- Autism
- Learning disorder
- Anxiety problems
- Learning difficulties
- Attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Bipolar disorder in children and adolescents
- Childhood depressions
- Defiance disorders
- School maturity
- Eating problems in children
- Tic disorders in children
Diagnosis of Psychiatric Diseases
The diagnosis of psychiatric disorders begins with the observation of behavioral and mood disorders. In this process, it is very important for the patient to share their symptoms and complaints with a specialized doctor. The diagnostic phase usually involves a combination of interviews, diagnostic examinations and psychometric tests. Diagnosis of psychiatric disorders is one of the cornerstones of the treatment process, as these illnesses often manifest themselves with certain symptoms. These symptoms play a critical role in making the correct diagnosis.
In the diagnostic process, it is also important to investigate the underlying causes of these disorders. Biological, physiological and hereditary factors are taken into account. Therefore, the guidance of a specialized physician is of great importance in order to make the correct diagnosis. Accurate diagnosis is an inevitable requirement for determining the appropriate treatment process and for the patient to regain his/her health.
Treatment of Psychiatric Diseases
Mental and physical health should be considered as a whole. It is as common for people to lose their physical health as it is for their mental health to deteriorate. In both cases, people can regain their health with the right diagnosis and treatment method. Deterioration of mental health leads to deterioration of physical health. Psychological problems manifest themselves with physical symptoms. Medication and psychotherapy are generally used to treat mental disorders.
Psychiatric drugs are not medicines that a person can use on their own. However, they can be recommended by a specialist in case of illness. Every person can be upset, but depression is a disorder and can be diagnosed by a specialist. An individualized treatment plan is then developed. Antidepressant medication used for long periods of time when it is not necessary is actually limited to certain situations. Another situation is when individuals who need it avoid medication, in which case they face the negative consequences of untreated mental illness. As with medication, the psychotherapy method should be determined and treatment should be planned with the advice of the attending physician. In this way, the success rate of treatment can be high.