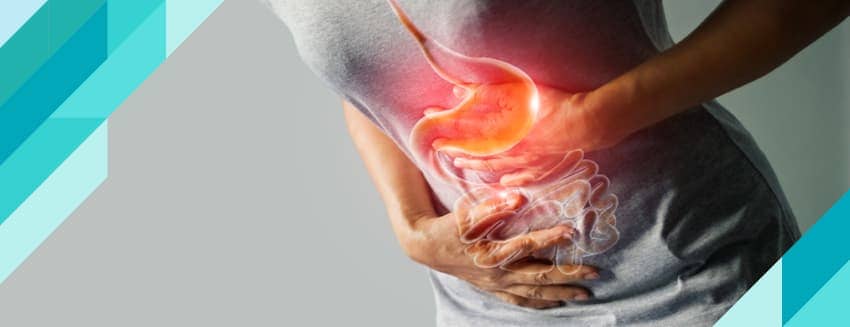
Gastritis is a collective term for a variety of inflammations of the stomach lining. It is often a direct result of infections with the bacterial species that cause stomach ulcers. It can also be caused by regular use of certain painkillers or too much alcohol consumption. The disease can occur in two stages. It can occur suddenly, or it can become chronic over a long period of time.
In some cases, it can lead to ulcers and an increased chance of stomach cancer. However, in most cases it is not seen as a condition that causes serious problems and recovery is possible with the correct application of treatments.
What are the Symptoms of Gastritis?
While the symptoms of gastritis may vary from person to person, there may be scraping, burning sensation or pain in the upper abdomen. These conditions may increase or decrease after a meal.
While patients may experience stomach problems, nausea, vomiting and fullness in the stomach after eating. It is also not the case that signs or symptoms will be seen in every case.
In some cases, it may progress without symptoms or signs and may appear after a long time. The problem of indigestion, which can be seen in most people, may be short-term in some cases and may pass spontaneously without requiring medical treatment.
In addition, if complaints and symptoms persist for more than a week, you should go to a doctor immediately.
In addition to stomach disorders, if blood comes from the person's mouth, if blood is observed in the stool after the toilet or if the color of the stool is black, a doctor should be seen and treated immediately.
What Causes Gastritis?
It is a disease that occurs as a result of any condition that can cause inflammation in the stomach lining. There may be many conditions among the causes of gastritis. As a result of any damage to the mucus that protects the inner wall of the stomach, damage to the stomach lining of the gastric juice, which is beneficial for digestion, can lead to infection.
In addition, an abnormally high number of inflammatory cells (Crohn's disease) and sarcoidosis, as well as many other diseases and medical conditions, can increase the risk of the disease.
Bacterial infections are the primary risk factor. In addition, although Helicobacter pylori is a common type of bacterial infection, upper gastrointestinal disorders occur in a minority of cases.
Experts believe that vulnerability to the bacteria may be due to genetic factors, smoking or changes in diet and lifestyle.
Regular use of painkillers can also cause acute and chronic illness. People who are constantly taking medication can damage the stomach wall, while it can also damage the substance that helps protect the stomach.
The lining of the stomach may become thinner with age and the likelihood of infections and autoimmune disorders may increase in elderly people. In addition, gastrointestinal diseases may also occur.
People who consume a lot of alcohol may have irritation and erosion of the stomach lining and are more likely to experience the disease. This disease condition can also occur when the immune system attacks its own cells.
While disease conditions and vitamin deficiency in some people can also lead to autoimmune diseases, these diseases include Hashimoto's disease, type 1 diabetes. Vitamin B12 deficiency is also linked to these conditions.
In addition, HIV and AIDS, Crohn's disease and certain parasitic infections can cause other medical conditions and this disease.
If the disease is not treated properly or if treatment is delayed, it can cause stomach ulcers or stomach bleeding. In rare chronic cases, cell changes in the stomach wall and lining can increase the risk of cancer.
How to Prevent Gastritis?
Although it is not certain how H. pylori infection, the most common type of the disease, spreads, there is some data that it can be transmitted from person to person through food or fluids.
Paying attention to personal hygiene, washing hands frequently with soap and water, cooking and consuming food completely can prevent this situation. To protect against different strains, one should act depending on the situation of that strain.
For example, measures such as reducing alcohol consumption or avoiding long-term use of painkillers prevent the development of the disease.
How is gastritis diagnosed?
In cases where the disease is suspected, you should see a doctor and be examined without wasting time. During the examination, the doctor may ask some questions to learn the patient's medical history in detail. Afterwards, some tests and examinations are performed to determine the cause of the disease.
During the diagnosis of gastritis, one of the tests performed is the H. pylori test. Depending on the severity of the condition, H. pylori bacteria can be detected by blood, stool or breath test.
For the breath test, the person is given a small glass of tasteless liquid containing radioactive carbon. The bacteria can break down this liquid in the stomach. The patient then has to blow into a transparent bag. The infection status is determined by the radioactive carbon in the breath.
The patients' upper digestive tract is examined in detail with the help of endoscopy. During the examination, it is examined whether there is any infection in the stomach or intestines.
If the doctor is suspicious, a small piece is taken and examined for a biopsy. The biopsy determines the presence of infection in the stomach.
X-rays of the upper digestive tract may be taken to detect abnormalities. The person is given a metallic liquid to drink in order to identify it. As a result of this method, the ulcerated tissue becomes more visible.
How is gastritis treated?
Gastritis treatment may differ from person to person depending on the condition of the disease. For example; The disease condition caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or alcohol can disappear in a short time by avoiding these substances.
In addition, gastritis medications can also be used in the treatment of the disease. Medicines should be used on doctor's prescription and doctor's advice. The person cannot apply a drug treatment on his/her own. It is aimed to end the bacteria with the treatment methods and medications recommended by the doctor.
The doctor may recommend some antibiotics for 1 or 2 weeks to be used when deemed necessary in cases.
In order to prevent the possibility of these bacteria developing resistance to the antibiotics and drugs used, it is important to use them for the period determined by the specialist and to use them without missing during this period.
Drugs that prevent the formation of stomach acid and provide healing benefits can also be used in the treatment process. Proton pump inhibitors, when recommended by the doctor, reduce and prevent the effect of cells that cause acid formation, even for a short time.
Their use in high doses may cause some problems. It can cause the possibility of fractures in the hip, wrist and spine. For this reason, it is recommended to be used only under the supervision of a doctor. Calcium supplements may be recommended during this process.
Any treatment other than the medications recommended by your doctor and the treatments your doctor deems necessary can worsen this condition and become unbearable. Stomach problems, which have an important place in the daily life of the person, can cause a lot of discomfort when left untreated.
In case of symptoms and complaints, the person should first be examined by specialist doctors and necessary tests should be performed.
